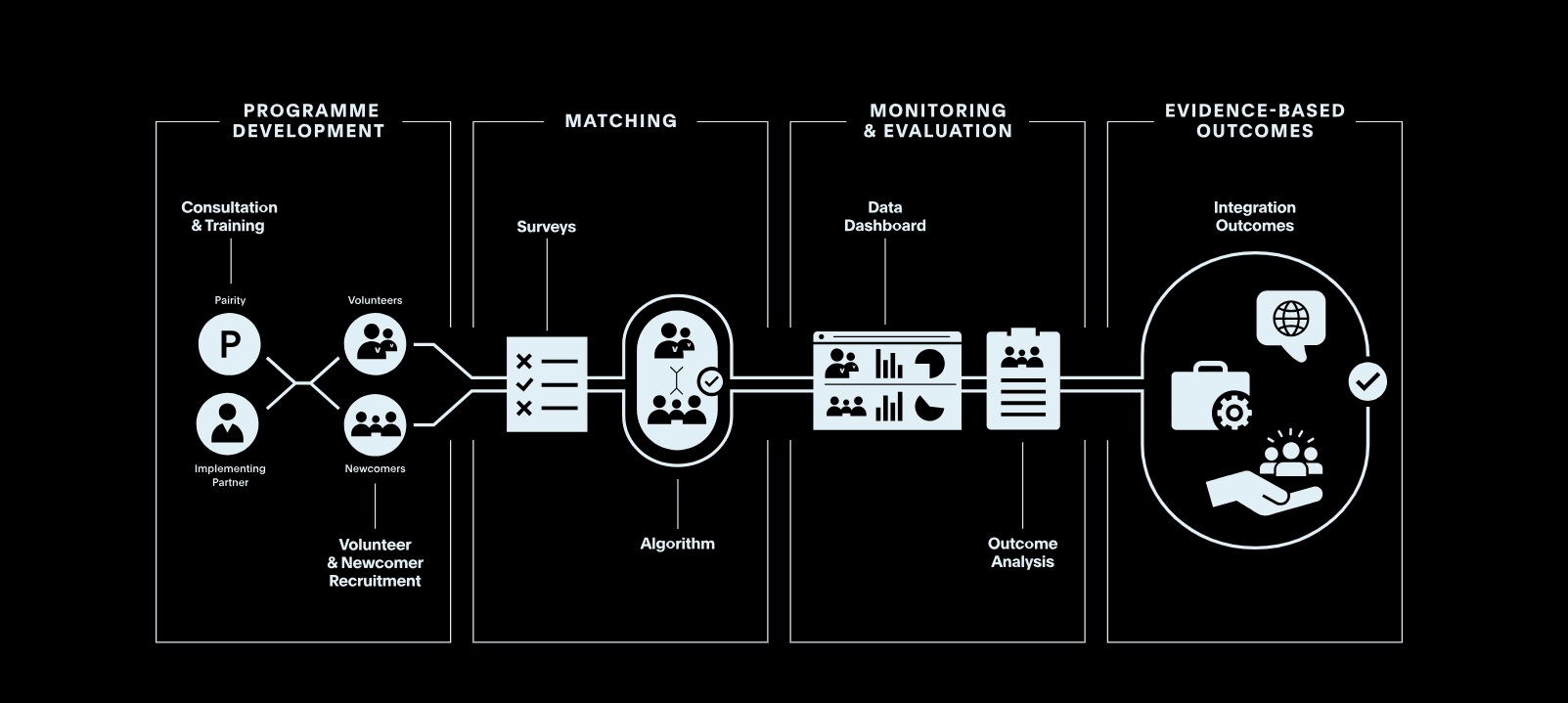
Structural barriers to the digital platform economy for forcibly displaced workers
Regulatory vacuums contribute to the structural exclusion of forcibly displaced populations seeking work on digital labour platforms. Even where these issues can be overcome, questions remain as to the viability of these platforms as a path to economic empowerment.